| Monthly Tech-Tip | Feb 14-15, 2026 - Major Server Upgrade Done | No tracking! No ads! |
Lead Bisilicate Frit
Description: Lead bisilicate frit
| Oxide | Analysis | Formula | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| PbO | 65.00% | 1.00 | |
| SiO2 | 35.00% | 2.00 | |
| Oxide Weight | 343.38 | ||
| Formula Weight | 343.38 | ||
Notes
This term refers to frits having one molar part of lead and two of silica. This ratio of silica and lead that is said to produce a stable low solubility powdered glass material that can be used in production with relative safety to workers.
In pottery circles, lead glazes carry a lot of “legal baggage” in North America, irresponsible use in the past contributed to this. Pottery supply companies do not carry lead bisilicate frits. Yet manufacturers have been using them all along and claim they can prove their recipes are resistant to leaching. Potters, especially on the hobby level, would not be good candidates for the use of lead bisilicate.
Ceraflux from Hammond Lead Products is the most common North American lead bisilicate. Many lead bisilicate frits contain from 1-3% Al2O3 and are referred to as "lead alumina bilsilicates". This addition further stabilizes the glass powder itself and helps prevent phase separation (crystallization) in the glass during firing.
For certain glazes, care must be taken not to ball-mill these frits too fine (eg. tin-glazed earthenware). Some products are dry milled by the manufacturer, others are wet milled (much less common).
While the frit powder itself is stable (compared to raw lead carbonate or oxide), that does not mean that glazes created using it automatically resist leaching. Theoretically, the most stable non-leachable glass would be created using the pure frit without additives (however our lead testing indicates lead leaching). To make a practical glaze slurry 10-15% clay is typically added, the add SiO2 and Al2O3 should add stability.
Lead borosilicate is different than lead bisilicate, the former has almost as much lead but the rest is a mix of B2O3, SiO2 and Na2O.
Related Information
Ferro Frit 3602 melt flow over many temperatures

This picture has its own page with more detail, click here to see it.
This demonstrates the amazing melt behaviour of lead-as-a-flux for ceramic glazes. Not only does it melt early, but it softens slowly over a 300F range of temperatures before it goes off the end of the runway on this GLFL test. Then, when fired 200F hotter than that, it remains a stable, clear and uncrazed glass. Beginning around 1750F, this becomes a transparent glaze, by itself.
Lead bisilicate with his ugly borosilicate cousins at a cone 05 party

This picture has its own page with more detail, click here to see it.
The middle front mug is glazed with an 85:15 lead bisilicate:kaolin mix, the G3971 recipe. It is an absolutely "knock your socks off" crystal-clear hyper-glossy surface that transmits the terra cotta color beautifully regardless of whether the clay is smooth or coarse or the glaze thick or thin (this one was applied as a brushing glaze in three coats on L215). My lead testing kit passes it with no detectable lead release. The other pieces are done using brush-on versions of boron-based clear glazes (commercial and made from a recipe). At almost any thickness and whether on L215 or L4170B clouding occurs. The worst one is a commercial three-coater on the right, the best is G1916W (it has 2% added iron as a fining agent for the micro-bubbles). My terra cotta plan: Glaze the inside functional surfaces with that and the outsides with the leaded one (and using a kiln exhaust system).
The secret of the higher gloss glaze on the right? A lead frit addition.

This picture has its own page with more detail, click here to see it.
These cone 04 glazes have the same recipe (a version of Worthington Clear sourcing B2O3 from Ulexite instead of Gerstley borate). But the one on the right is more glassy, more transparent. Why? It has 10% added lead bisilicate frit. Lead bisilicate produces dazzling transparent glazes. no other method matches it. While potters gasp at the thought of using lead consider this: They thrive on unstable flux-deprived, glass-deprived and alumina-deprived base stoneware glazes with additions of large percentages of toxic colorants like chrome and manganese!
A lead bisilicate frit fails a leach test. Yet as-a-glaze it passes. Why?
I have soaked a lead bisilicate frit in vinegar overnight. To test whether it is leaching I pour the vinegar leachate into a test tube, soak a Q-Tip in the sensor solution and dip it into the vinegar. It turns black immediately - so we have lead in the leachate! But this is not as it seems.
Remember a key point here: The frit glass had no opportunity to be annealed - it was crash-cooled by being quenched in water. Annealing and associated toughening of the surface is a natural consequence of a glaze cooling slowly in a periodic kiln - which is why pieces made using an 85:15 mix of this same frit and kaolin, pass this test. The same 85:15 mix also still passes a lead check test if melted into an ingot and crushed into a granular powder (this is amazing given the exponential increase in surface area).
Is a brilliant metallic glaze surface possible without lead bisilicate?
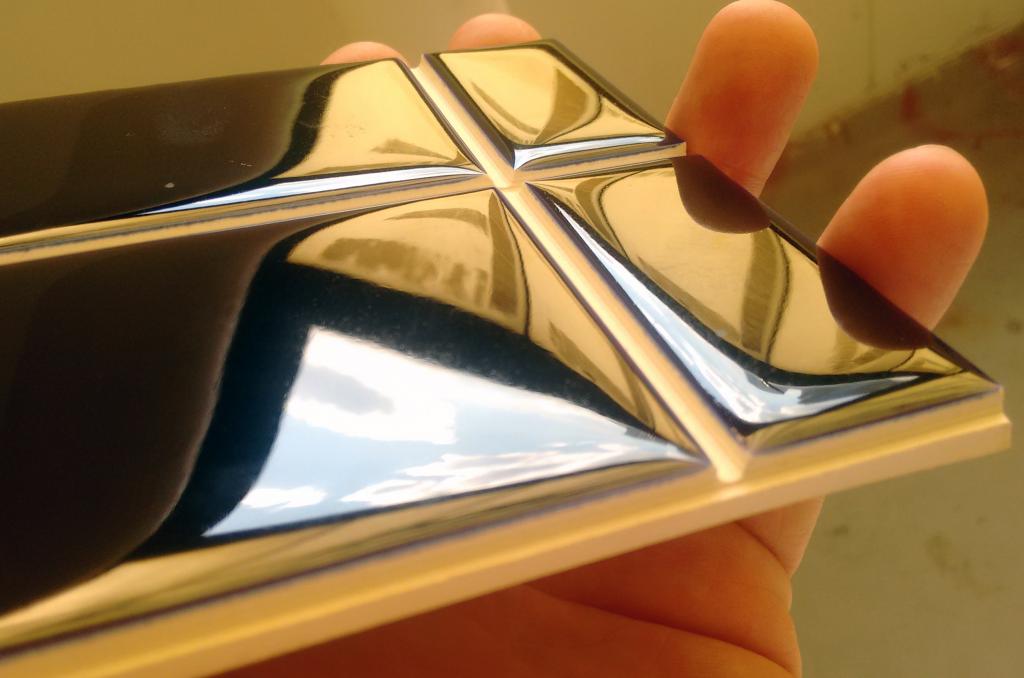
This picture has its own page with more detail, click here to see it.
Lead glazes can have brilliant high gloss surfaces. They can dissolve high percentages of colorants without losing transparency. And do this at unbelievably low temperatures. In Europe the use of lead is still common among potters, in North America it’s use is often met with fear. This picture is courtesy of Cory Lund. He glazes the tiles, cuts the grooves and then fires the tiles again. While working in an area where lead frits are not available Mr. Lund was able to produce a similar surface using lead free Fusion Frit FZ-16, albeit with higher thermal expansion and thus some crazing (but it was not an issue for him). Then, when the frit was not available, he was able to calculate the chemistry and source it using Borax, this worked so well the glaze was even melting too much!
Links
| Materials |
Lead Sesquisilicate Frit
A standard frit of 1 molar part of PbO and 1.5 of SiO2. It melts lower than a lead bisilicate. |
| Materials |
Frit
Frits are made by melting mixes of raw materials, quenching the melt in water, grinding the pebbles into a powder. Frits have chemistries raw materials cannot. |
| Materials |
Ferro Frit 3498
|
| Materials |
Pemco Frit Pb-700
|
| Materials |
Potclays Frit 2261
|
| Materials |
Ferro Frit 3602
|
| Materials |
Solargil Frit FR2
|
| Materials |
Ferro Frit 4064
|
| Materials |
Ferro Frit 4364
|
| Materials |
Ceraflux
An alumina lead bisilicate from Hammond Lead Products in Indiana. The data sheet claims it is safe and insoluble in stomach acid. |
| Materials |
PotteryCrafts Frit P2950
|
| Materials |
Pemco Frit Pb-545
|
| Materials |
P29 Frit
|
| Materials |
Ceraflux
|
| Materials |
Lead Bisilcate B-15
|
| Materials |
Hommel Frit 437
|
| Materials |
BPS Lead Bisilicate
|
| Materials |
Lead Monosilicate Frit
A standard frit of 1 molar part of PbO and 1 of SiO2. It melts lower than a lead bisilicate. |
| Materials |
Frit Welte FR 2015
|
| Materials |
Ceradel Frit C 1249
|
| Materials |
Ceradel Frit C 1250
|
| Materials |
Ceradel Frit C 1251
|
| Materials |
Ferro Frit 3403
|
| Materials |
Red Lead
|
| Materials |
Lead Carbonate
|
| Materials |
Ferro Frit CE VTR 29
|
| Materials |
Frit 3647
|
| Hazards |
Lead Toxicology
|
| Hazards |
Lead in Ceramic Glazes
Lead glazes may or may not be hazardous. This topic is not as clear as you might think. |
| Typecodes |
Leaded Frit
Frits can contain 1% or 80% PbO so this category can be misleading, check the chemistry to find out. |
| Typecodes |
Frit
A frit is the powdered form a man-made glass. Frits are premelted, then ground to a glass. They have tightly controlled chemistries, they are available for glazes of all types. |
| Glossary |
Metallic Glazes
Non-functional ceramic glazes having very high percentages of metallic oxides/carbonates (manganese, copper, cobalt, chrome). |
| Glossary |
Lead in Ceramic Glazes
Lead is a melter in ceramic glazes and performs exceptionally well and must be misused to be toxic. It is also now environmentally pervasive. It is toxic and cumulative at any level of exposure. |
Data
| Co-efficient of Linear Expansion | 7.1 x 10-6 |
|---|---|
| Frit Softening Point | 880-1050C M |
| Frit Softening Point | 1390F |
| By Tony Hansen Follow me on        |  |
Got a Question?
Buy me a coffee and we can talk

https://digitalfire.com, All Rights Reserved
Privacy Policy
