| Monthly Tech-Tip | Feb 14-15, 2026 - Major Server Upgrade Done | No tracking! No ads! |
Custer Feldspar
Alternate Names: Custer Spar
Description: Potash Feldspar
| Oxide | Analysis | Formula | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| CaO | 0.30% | 0.03 | |
| K2O | 10.00% | 0.66 | |
| Na2O | 3.00% | 0.30 | |
| Al2O3 | 17.00% | 1.04 | 16.5 min |
| SiO2 | 68.50% | 7.13 | |
| Fe2O3 | 0.10% | - | 0.05 |
| LOI | 0.30% | n/a | |
| Oxide Weight | 618.54 | ||
| Formula Weight | 620.40 | ||
Notes
In 2024 this material is not available and their website is not working. Little information online about what happened. G200 or Mahavir feldspars can be substituted in most cases, they are lower in iron and should produce as good or better results in most glazes or bodies. If the percentage is high or your feldspar has a significantly different chemistry calculations can be done to compensate (see video demo link below).
This is one of the main feldspars used in the ceramic industry in North America. It is used in industries such as abrasives, sanitary ware, floor and wall tile, dinnerware, pottery, and electrical porcelain. It is a ceramic grade, high potash feldspar and is available in crude, 200, 325 mesh and chip form.
Since the 2000s we have been getting independent reports of a significant reduction in the potash content and increase is SiO2 (compared to that stated on the the official data sheet). Traditionally Pacer, the manufacturer, has reported KNaO as around 13%. However independent testing done (e.g. by Ron Roy and others) suggested that around the year 2000 the K2O content dropped to about 7.5 (with no accompanying change in the Na2O). Pacer disputed this. The chemical analyses they provided with individual shipments of material continued to report chemistries similar to those stated on their datasheet. Additionally, they had a page on their website named "Clarification of Custer Feldspar Chemical Composition Data" in which they claimed their analysis was always accurate. Whether justified or not, Custer Feldspar became somewhat of a scapegoat, people blaming it when online recipes they try do not work!
Since 2021 their data sheet for the P325 grade is claiming SiO2 - 67.6, Al2O3 - 17.2, Fe2O3 - 0.1, K2O - 10, Na2O - 4.5, CaO - 0.3, LOI - 0.3. This represents an increase in the Na2O content, so one might expect it to melt better than in the recent past.
As with any feldspar, production users should be vigilant to do sieve analysis testing to spot any iron-bearing particles in the plus 100 mesh range. A melt fluidity test is also practical to gauge its behavior as a flux.
Related Information
Original container bag of Custer Feldspar

This picture has its own page with more detail, click here to see it.
The back of the bag is blank. The warning label on the front mentions feldspar, crystalline silica and mica.
Custer Feldspar 2021 data sheet

This picture has its own page with more detail, click here to see it.
It is worth noting that ceramics is not among the recommended applications for this material. The Pacer Minerals website does not have information that indicates there are multiple grades having different chemistries.
Which is the champion melter of American/Canadian feldspars?
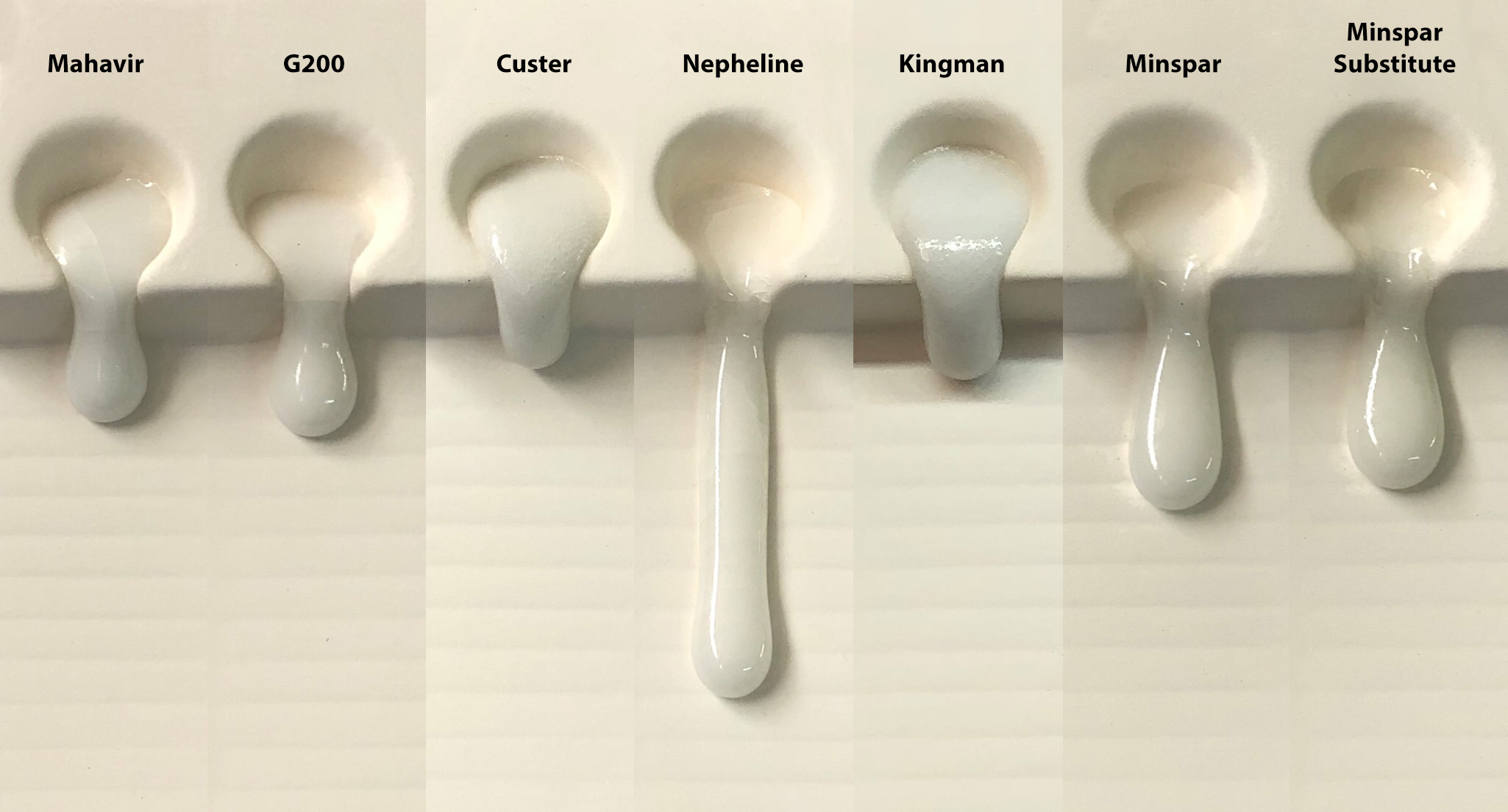
This picture has its own page with more detail, click here to see it.
Feldspars are employed in glaze recipes as melters. So comparing their melt fluidities should be helpful in deciding if one can substitute for another (of course, if possible, a soda-predominant feldspar should be substituted for another soda spar). Feldspars don't melt alone at cone 6 (2200F) so we mixed each with 15% Ferro Frit 3195 (we consider a feldspar a material that sources KNaO). Nepheline Syenite, this is A270, is the champion melter here. Other similar ones can be spotted easily. In the end, degree of melt is a valid consideration in determining if one feldspar is a viable substitute for another in a recipe. Even if the feldspar you want to substitute does not melt as much a little frit can be added to the recipe to make up for the difference (e.g. 3-5%).
Feldspars, the primary high temperature flux, melt less than you think.

This picture has its own page with more detail, click here to see it.
Our melt fluidity tester is being used to compare cone 8 melt fluidities of Custer, G-200 and i-Minerals high soda and high potassium feldspars. Notice how little the pure materials are moving (bottom), even though they are fired to cone 11. In addition, the sodium feldspars move better than the potassium ones. But feldspars do their real fluxing work when they can interact with other materials. As a demonstration of that, note how well they flow with only 10% frit added (top), even though fired three cones lower.
Comparing the melt fluidity of two shipments of Custer Feldspar

This picture has its own page with more detail, click here to see it.
A GLFL test for melt-flow to compare Custer Feldspar from Feb/2012 (right) with Mar/2011 (fired at cone 6). Custer Feldspar does not melt like this by itself at cone 10. It was mixed 80:20 Feldspar:Ferro Frit 3134. This test demonstrates that the material has been very consistent between these two shipments.
Custer Feldspar vs Nepheline Syenite at cone 8 oxidation

This picture has its own page with more detail, click here to see it.
Although Nepheline Syenite and Custer Feldspar are used as effective body maturing agents and fluxes in glazes past cone 6, curiously, neither of them melt well by themselves. Thus, both of these come 6 melt fluidity tests add 20% Ferro Frit 3134 to get them flowing. This is a 2021 shipment of the feldspar and a 2022 shipment of the nepheline.
Replace Custer Feldspar in a cone 10R glaze recipe in 2 minutes

This picture has its own page with more detail, click here to see it.
Our G2571A and G1947U cone 10R glaze recipes are both in use in Ecuador. One user has been importing Custer feldspar, but cannot get it and needs to substitute a local feldspar. That material is much higher in SiO2 and much lower in Al2O3 and KNaO (so a pound-for-pound substitution is not going to work). Here is how I used my account at insight-live.com to figure out what to do. It turned out to be a matter of increasing the new feldspar to match the KNaO matched (which also matched the Al2O3) and then reducing the silica to match the SiO2 match. The amount by which I had to change the feldspar is a testament to how different the chemistry of these materials can be from country to country.
Links
| URLs |
http://www.pacerminerals.com/msds1.html
MSDS |
| URLs |
http://www.pacerminerals.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/FELDSPAR-200-325-Tech-Data.pdf
Custer Data Sheet |
| URLs |
http://www.pacerminerals.com/prodcomp.html
Product Reference Guide |
| URLs |
http://www.pacerminerals.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/Feldspar_Tech_Data_Clarification.pdf
Clarification of Custer Feldspar Chemical Composition from Pacer |
| URLs |
https://digitalfire.com/4sight/datasheets/SDSCusterFeldspar.pdf
Custer Feldspar SDS |
| Materials |
Eureka Feldspar
|
| Materials |
Kingman Feldspar
|
| Materials |
Chesterfield Feldspar
|
| Materials |
G-200 Feldspar
|
| Materials |
Feldspar
In ceramics, feldspars are used in glazes and clay bodies. They vitrify stonewares and porcelains. They supply KNaO flux to glazes to help them melt. |
| Materials |
Potash Feldspar
A feldspar having a KNaO content that predominates in potassium. |
| Materials |
MC 200K Feldspar
|
| Materials |
Mahavir Potash Feldspar
|
| Materials |
Fortispar
|
| Typecodes |
Feldspar
The most common source of fluxes for high and medium temperature glazes and bodies. |
| Hazards |
Feldspar
Feldspars are abundant and varied in nature. They contain small amounts of quartz (while nepheline syenite does not). |
| Media |
Substituting Custer Feldspar for Another in a Cone 10R Glaze Recipe
A locally available feldspar contains much less KNaO and Al2O3 and much more SiO2 than Custer Feldspar. Here is a step-by-step method, using my account at insight-live.com, to alter the recipe so that the overall chemistry of the glaze is maintained. |
Data
| Sieve Analysis 35-325 Wet | 0.3% (0.5% max) |
|---|---|
| Sieve Analysis 35-325 Wet | 100 |
| Sieve Analysis 35-325 Wet | 4% (5% max) |
| Density (Specific Gravity) | 2.6 |
| pH for dry powder | 8.0 |
| By Tony Hansen Follow me on        |  |
Got a Question?
Buy me a coffee and we can talk

https://digitalfire.com, All Rights Reserved
Privacy Policy
